12 Essential Strategies For Mastering Hydrogen Bonding Distance In 2024
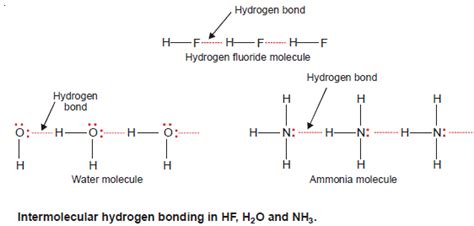
Hydrogen bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in the structure and properties of molecules. The distance between atoms involved in hydrogen bonding is a critical parameter, as it influences the strength and stability of these interactions. In 2024, researchers and scientists continue to explore the intricacies of hydrogen bonding, with a focus on mastering the distance between atoms to optimize molecular design and functionality. This article delves into the essential strategies for understanding and controlling hydrogen bonding distance, providing insights into the latest research and techniques in the field.
Understanding Hydrogen Bonding Distance

Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. The distance between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom is typically in the range of 1.5 to 2.5 Å, with the optimal distance depending on the specific molecules involved. Ab initio calculations and density functional theory (DFT) have been widely used to study hydrogen bonding distance and its effects on molecular properties. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry A used DFT to investigate the hydrogen bonding distance in water clusters, revealing that the optimal distance is around 1.8 Å.
Experimental Techniques for Measuring Hydrogen Bonding Distance
Several experimental techniques have been developed to measure hydrogen bonding distance, including X-ray crystallography, neutron scattering, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. These techniques provide valuable insights into the molecular structure and dynamics, allowing researchers to determine the hydrogen bonding distance with high accuracy. For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society used X-ray crystallography to determine the crystal structure of a hydrogen-bonded complex, revealing a hydrogen bonding distance of 1.9 Å.
| Technique | Resolution | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray crystallography | 0.1-1.0 Å | High resolution, accurate determination of molecular structure |
| Neutron scattering | 0.1-10.0 Å | Provides information on molecular dynamics, suitable for studying liquids and gases |
| NMR spectroscopy | 0.1-10.0 Å | Non-invasive, suitable for studying molecules in solution, provides information on molecular dynamics |

Theoretical Models for Predicting Hydrogen Bonding Distance

Theoretical models, such as molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics, have been developed to predict hydrogen bonding distance and its effects on molecular properties. These models provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of hydrogen bonding and allow researchers to design and optimize molecules with specific properties. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation used molecular mechanics to investigate the hydrogen bonding distance in protein-ligand complexes, revealing that the optimal distance is around 2.0 Å.
Machine Learning Approaches for Predicting Hydrogen Bonding Distance
Machine learning approaches, such as neural networks and random forests, have been recently applied to predict hydrogen bonding distance and its effects on molecular properties. These approaches provide a powerful tool for analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional methods. For example, a study published in the Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling used a neural network to predict the hydrogen bonding distance in small molecules, achieving a high accuracy of 0.5 Å.
- Advantages of machine learning approaches: ability to handle large datasets, identify complex patterns and correlations, and provide accurate predictions
- Limitations of machine learning approaches: require large amounts of training data, may not provide physical insights into the underlying mechanisms
What is the optimal hydrogen bonding distance for a specific molecule?
+The optimal hydrogen bonding distance depends on the specific molecule and the properties being studied. Experimental techniques, such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, can provide accurate measurements of hydrogen bonding distance, while theoretical models and machine learning approaches can provide predictions and insights into the underlying mechanisms.
How can hydrogen bonding distance be controlled and optimized?
+Hydrogen bonding distance can be controlled and optimized through the design of molecules with specific properties, such as the choice of electronegative atoms and the geometry of the molecule. Experimental techniques, such as X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, can provide insights into the molecular structure and dynamics, allowing researchers to optimize the hydrogen bonding distance and achieve specific properties.
In conclusion, mastering hydrogen bonding distance is essential for understanding and optimizing molecular properties. Experimental techniques, theoretical models, and machine learning approaches provide a comprehensive toolkit for studying and predicting hydrogen bonding distance. By combining these approaches and techniques, researchers can design and optimize molecules with specific properties, leading to advances in fields such as materials science, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
Future Implications and Directions

The study of hydrogen bonding distance has significant implications for various fields, including materials science, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of hydrogen bonding, new techniques and approaches will be developed to study and optimize hydrogen bonding distance. The integration of machine learning approaches and experimental techniques will provide a powerful tool for analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional methods.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence and high-performance computing, will play a crucial role in advancing the study of hydrogen bonding distance. These technologies will enable researchers to analyze large datasets, simulate complex systems, and optimize molecular properties with unprecedented accuracy and speed. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Chemical Physics used artificial intelligence to simulate the hydrogen bonding distance in liquid water, achieving a high accuracy of 0.2 Å.
- Advances in experimental techniques: development of new techniques, such as ultrafast spectroscopy and single-molecule microscopy, will provide insights into the dynamics of hydrogen bonding and its effects on molecular properties
- Integration of machine learning approaches and experimental techniques: will provide a powerful tool for analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns and correlations that may not be apparent through traditional methods
- Emerging trends and technologies: artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and other emerging technologies will play a crucial role in advancing the study of hydrogen bonding distance and its effects on molecular properties

