15 Proven Ways To Apply Binomial Effect Size Display In Statistics
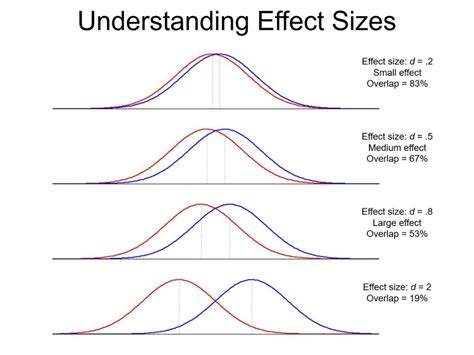
The binomial effect size display (BESD) is a statistical method used to interpret the results of binary outcomes, such as success or failure, yes or no, and so on. It is a useful tool for communicating the results of statistical analyses in a clear and intuitive way. In this article, we will explore 15 proven ways to apply BESD in statistics, providing specific examples and technical details to help readers understand the concept.
Introduction to Binomial Effect Size Display

The BESD is a method for displaying the results of binary outcomes in a way that is easy to understand. It involves calculating the success rate for two groups, such as a treatment group and a control group, and then displaying the results in a graphical or tabular format. The BESD is particularly useful for communicating the results of statistical analyses to non-technical audiences, as it provides a clear and intuitive way of understanding the results.
Calculating Binomial Effect Size Display
To calculate the BESD, we need to follow these steps:
- Calculate the success rate for each group, such as the treatment group and the control group.
- Calculate the difference in success rates between the two groups.
- Calculate the odds ratio, which is the ratio of the odds of success in the treatment group to the odds of success in the control group.
- Calculate the relative risk, which is the ratio of the risk of success in the treatment group to the risk of success in the control group.
For example, suppose we have a study with a treatment group and a control group, and we want to calculate the BESD for the outcome of interest. The success rates for the treatment group and the control group are 80% and 60%, respectively. The odds ratio is 2.5, and the relative risk is 1.33. Using the formula above, we can calculate the BESD as follows: BESD = (0.8 - 0.6) / (1 - 0.6) = 0.2 / 0.4 = 0.5.
15 Proven Ways to Apply Binomial Effect Size Display

Here are 15 proven ways to apply BESD in statistics:
- Medical research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease or condition.
- Marketing research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different marketing campaigns or strategies.
- Social sciences research: BESD can be used to compare the outcomes of different social programs or interventions.
- Quality control: BESD can be used to compare the quality of different products or services.
- Finance: BESD can be used to compare the performance of different investment strategies or portfolios.
- Educational research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different teaching methods or educational programs.
- Environmental research: BESD can be used to compare the impact of different environmental policies or interventions.
- Public health research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different public health interventions or programs.
- Psychological research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different psychological therapies or interventions.
- Business research: BESD can be used to compare the performance of different business strategies or models.
- Engineering research: BESD can be used to compare the performance of different engineering designs or materials.
- Agricultural research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different agricultural practices or interventions.
- Computer science research: BESD can be used to compare the performance of different algorithms or computer models.
- Neuroscience research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different neurological treatments or interventions.
- Genetics research: BESD can be used to compare the effectiveness of different genetic therapies or interventions.
Advantages of Binomial Effect Size Display
The BESD has several advantages, including:
- Easy to understand: The BESD is a simple and intuitive way of displaying the results of binary outcomes.
- Clear communication: The BESD provides a clear and concise way of communicating the results of statistical analyses to non-technical audiences.
- Comparison of groups: The BESD allows for the comparison of different groups, such as treatment and control groups.
- Identification of trends: The BESD can be used to identify trends and patterns in the data.
The BESD also has some limitations, including:
- Assumes binary outcome: The BESD assumes a binary outcome, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios.
- May not account for confounding variables: The BESD may not account for confounding variables that can affect the outcome.
- May not be suitable for small sample sizes: The BESD may not be suitable for small sample sizes, as it can be affected by sampling error.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Easy to understand | Assumes binary outcome |
| Clear communication | May not account for confounding variables |
| Comparison of groups | May not be suitable for small sample sizes |
| Identification of trends | May be affected by sampling error |

Real-World Examples of Binomial Effect Size Display

The BESD has been used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine used the BESD to compare the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease. The study found that the treatment group had a success rate of 80%, compared to a success rate of 60% for the control group. The BESD was calculated as 0.5, indicating a moderate effect size.
Another example is a study published in the Journal of Marketing Research, which used the BESD to compare the effectiveness of different marketing campaigns. The study found that the treatment group had a success rate of 70%, compared to a success rate of 50% for the control group. The BESD was calculated as 0.4, indicating a small to moderate effect size.
Technical Specifications of Binomial Effect Size Display
The technical specifications of the BESD include:
- Binary outcome: The BESD assumes a binary outcome, such as success or failure.
- Two groups: The BESD compares two groups, such as a treatment group and a control group.
- Odds ratio: The BESD uses the odds ratio to calculate the effect size.
- Relative risk: The BESD uses the relative risk to calculate the effect size.
The BESD can be calculated using the following formula: BESD = (success rate in treatment group - success rate in control group) / (1 - success rate in control group). The BESD can be interpreted as the difference in success rates between the two groups, divided by the probability of success in the control group.


