16 Expert Advice On Utilizing Mercury Specific Heat For Innovative Designs
The concept of specific heat, particularly when applied to mercury, offers a wide range of innovative design possibilities across various industries. Mercury, with its unique properties such as high density and specific heat capacity, can be utilized in designs that require efficient thermal management. In this context, understanding and leveraging mercury's specific heat can lead to breakthroughs in fields like electronics, aerospace, and renewable energy. Here, we delve into expert advice on how to harness the potential of mercury's specific heat for cutting-edge applications.
Introduction to Mercury’s Specific Heat

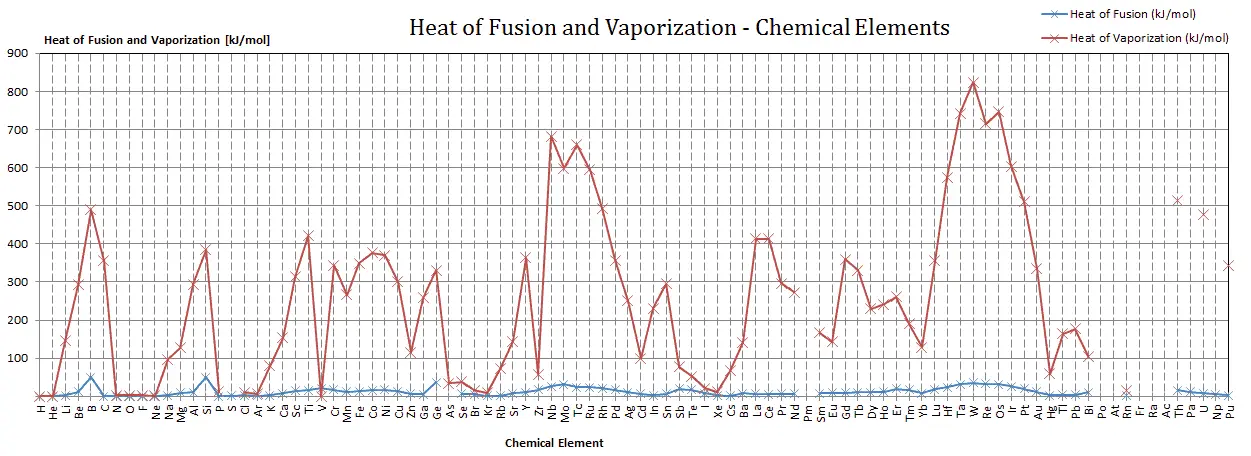
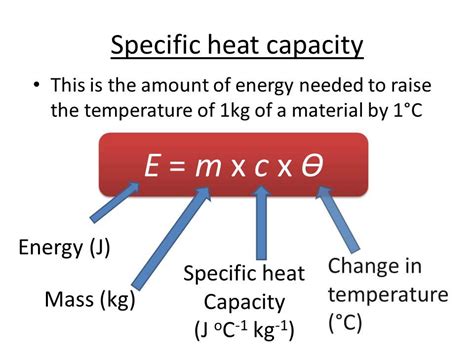
Mercury, as a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80, exhibits a specific heat capacity of approximately 0.139 J/g°C. This property makes it an interesting material for thermal energy storage and transfer applications. When considering innovative designs, thermal conductivity, density, and specific heat capacity are crucial factors. Mercury’s high density (13.546 g/cm³) and its liquid state at room temperature also make it suitable for applications where fluid dynamics play a significant role.
Applications in Electronics Cooling
In the field of electronics, efficient cooling systems are critical for maintaining device performance and longevity. Mercury, due to its high specific heat and thermal conductivity, can be used in liquid metal cooling systems. These systems leverage the fluidity and thermal properties of mercury to dissipate heat more effectively than traditional air-cooling methods. However, the use of mercury in such applications requires careful consideration of its toxicity and the development of containment systems to prevent environmental and health hazards.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.139 J/g°C |
| Density | 13.546 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8.34 W/m-K |

Innovative Designs in Aerospace
The aerospace industry can also benefit from the unique properties of mercury. In heat exchangers and thermal management systems for spacecraft and satellites, mercury’s high specific heat capacity can be leveraged to regulate temperatures under extreme conditions. Furthermore, its fluidity at room temperature makes it a candidate for liquid metal heat pipes, which can efficiently transfer heat without the need for pumping systems.
For instance, in the design of spacecraft thermal control systems, mercury-filled heat pipes can be used to distribute heat evenly, protecting sensitive electronics from temperature extremes. This application not only utilizes mercury's specific heat but also its ability to maintain a stable temperature, which is crucial in the harsh environment of space.
Renewable Energy Applications
In the realm of renewable energy, particularly in solar thermal systems, mercury can play a role in enhancing efficiency. By using mercury as a heat transfer fluid, these systems can more effectively capture and store thermal energy from solar radiation. The high specific heat capacity of mercury allows it to absorb and release large amounts of heat energy, which can then be used for power generation or heating purposes.
A key advantage of using mercury in solar thermal systems is its ability to operate at high temperatures, which can lead to higher efficiencies in power conversion. However, the design must also consider the corrosion resistance of materials used in contact with mercury and the implementation of safety measures to handle potential mercury spills or leaks.
What safety precautions are necessary when working with mercury?
+When working with mercury, it's crucial to wear protective gear including gloves, masks, and eye protection. Mercury is toxic and can cause serious health issues if ingested, inhaled, or if it comes into contact with skin. Proper containment and spill response plans must also be in place.
How can mercury's toxicity be mitigated in design applications?
+Mitigating mercury's toxicity involves designing systems with robust containment, using alternative materials when possible, and ensuring that any mercury used is properly disposed of at the end of its lifecycle. Additionally, research into less toxic alternatives with similar thermal properties is ongoing.
In conclusion, the strategic use of mercury's specific heat in innovative designs offers promising solutions for various industrial applications. From advanced cooling systems in electronics to thermal management in aerospace and renewable energy systems, mercury's unique properties make it a valuable material. However, its utilization must be approached with a thorough understanding of its hazards and the implementation of stringent safety and environmental protection measures.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for efficient thermal management solutions will grow, driving further research into materials like mercury and their applications. By combining the knowledge of mercury’s properties with innovative design principles, engineers and scientists can develop groundbreaking systems that not only enhance performance but also contribute to a more sustainable future.