18 Complete Guides To Measuring Pka Of Hydronium For Better Results

Measuring the pKa of hydronium is a crucial aspect of understanding the behavior of acids in aqueous solutions. The pKa value is a measure of the strength of an acid, with lower values indicating stronger acids. In the case of hydronium (H3O+), its pKa value is a fundamental constant that plays a significant role in various chemical and biochemical processes. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of measuring pKa of hydronium, exploring the theoretical background, experimental methods, and best practices for obtaining accurate results.
Theoretical Background

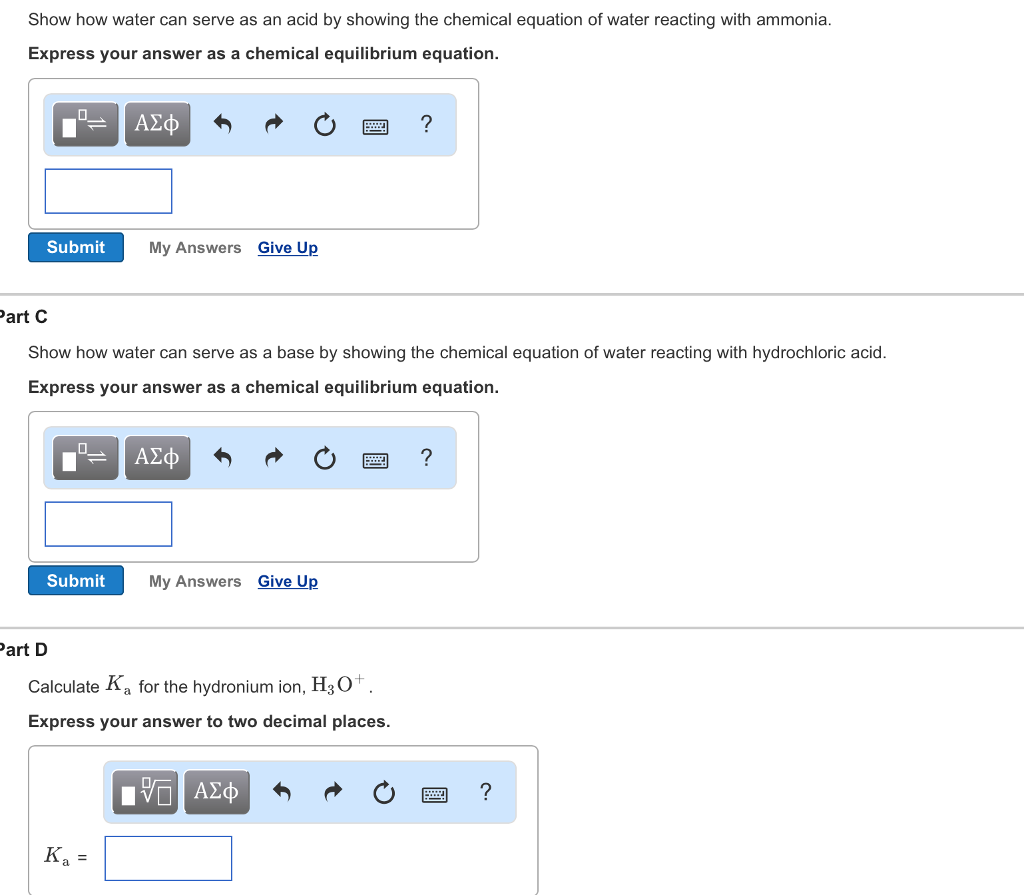
The pKa of hydronium is defined as the negative logarithm of the equilibrium constant (Ka) for the dissociation of hydronium into hydrogen ions (H+) and water molecules. The dissociation reaction is represented by the equation: H3O+ ⇌ H+ + H2O. The pKa value is calculated using the formula: pKa = -log10(Ka). The Ka value for hydronium is approximately 1.0 × 10^(-1.74) at 25°C, which corresponds to a pKa value of around -1.74.
Importance of pKa in Chemical Reactions
The pKa value of hydronium has significant implications for various chemical reactions, particularly those involving acid-base catalysis. A strong acid like hydronium can donate protons (H+) to other molecules, influencing the reaction kinetics and equilibrium. Understanding the pKa of hydronium is essential for predicting the behavior of acids in solution, designing effective catalysts, and optimizing reaction conditions.
| pKa Value | Temperature (°C) | Ka Value |
|---|---|---|
| -1.74 | 25 | 1.0 × 10^(-1.74) |
| -1.71 | 30 | 1.0 × 10^(-1.71) |
| -1.77 | 20 | 1.0 × 10^(-1.77) |

Experimental Methods for Measuring pKa
Several experimental methods can be employed to measure the pKa of hydronium, including potentiometric titration, spectroscopy, and chromatography. Potentiometric titration involves measuring the potential difference between two electrodes as a function of the acid concentration. Spectroscopic methods, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, can provide information on the molecular structure and environment of the hydronium ion. Chromatographic techniques, like ion exchange chromatography, can separate and quantify different ionic species, including hydronium.
Potentiometric Titration
Potentiometric titration is a widely used method for measuring the pKa of hydronium. The technique involves adding a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), to a solution of hydronium and measuring the potential difference between two electrodes, typically a glass electrode and a reference electrode. The potential difference is related to the concentration of hydronium ions, allowing for the calculation of the pKa value.
The experimental setup for potentiometric titration typically consists of a thermostatted cell, a pH meter, and a burette for adding the titrant. The glass electrode is a critical component, as it responds to changes in the hydronium ion concentration. The calibration of the electrode is essential to ensure accurate measurements.
| Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Potentiometric Titration | High accuracy, simple setup | Requires calibration, sensitive to temperature |
| Spectroscopy (NMR, IR) | Provides molecular information, non-invasive | Requires specialized equipment, may not be suitable for all samples |
| Chromatography (Ion Exchange) | Separates and quantifies ionic species, high resolution | Requires specialized equipment, may not be suitable for all samples |
Best Practices for Measuring pKa
To obtain accurate and reliable pKa values, it’s essential to follow best practices in experimental design, data analysis, and result interpretation. Some key considerations include:
- Temperature control: Maintain a constant temperature throughout the experiment, as small changes can significantly affect the pKa value.
- Calibration and validation: Ensure that all equipment is properly calibrated and validated before use.
- Sample preparation: Prepare samples carefully, avoiding contamination and ensuring that the hydronium ion is in its desired state.
- Data analysis: Use robust statistical methods to analyze data and calculate the pKa value.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Measuring the pKa of hydronium can be challenging due to various factors, such as temperature fluctuations, electrode calibration issues, and sample contamination. To overcome these challenges, researchers can employ strategies like:
- Using thermostatted cells to maintain a constant temperature.
- Regularly calibrating electrodes to ensure accuracy.
- Purifying samples to minimize contamination.
What is the significance of pKa in chemical reactions?
+The pKa value of hydronium is crucial in understanding the behavior of acids in aqueous solutions, as it influences the reaction kinetics and equilibrium. A strong acid like hydronium can donate protons to other molecules, affecting the reaction outcome.
How can I choose the most suitable experimental method for measuring pKa?
+Consider the specific requirements of your research question, including the desired level of accuracy, the nature of the sample, and the availability of equipment. Potentiometric titration, spectroscopy, and chromatography are common methods, each with its advantages and limitations.
In conclusion, measuring the pKa of hydronium is a complex task that requires careful consideration of theoretical background, experimental methods, and best practices. By understanding the significance of pKa in chemical reactions, selecting the most suitable experimental method, and following best practices, researchers can obtain accurate and reliable pKa values, advancing our knowledge of acid-base chemistry and its applications.


