How Does Hydrogen Bonding Distance Affect Chemical Reactions In 2025 Research
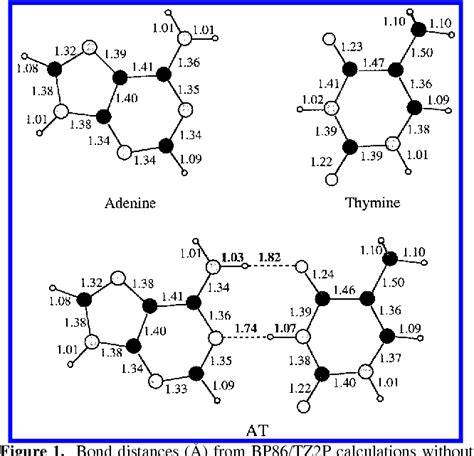
Hydrogen bonding is a crucial aspect of chemical interactions, playing a significant role in the structure and function of molecules. The distance between atoms involved in hydrogen bonding can significantly impact the strength and nature of these interactions, ultimately influencing chemical reactions. In 2025, research has continued to uncover the complexities of hydrogen bonding and its effects on chemical processes. This article delves into the current understanding of how hydrogen bonding distance affects chemical reactions, highlighting recent findings and their implications for various fields.
Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding
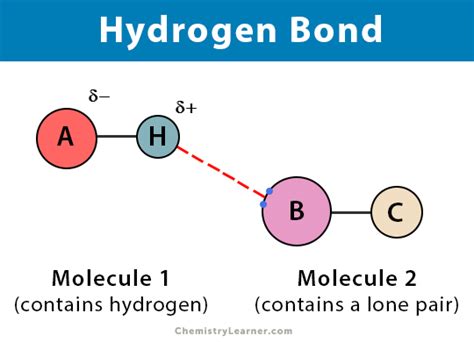
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. This electronegative atom pulls the shared electrons closer, leaving the hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge. As a result, the hydrogen atom can form a weak bond with another electronegative atom in a nearby molecule. The strength of hydrogen bonds is significantly influenced by the distance between the atoms involved, with shorter distances generally leading to stronger interactions.
Factors Influencing Hydrogen Bonding Distance
The distance between atoms in a hydrogen bond is affected by several factors, including the electronegativity of the atoms involved, the bond angle, and the polarity of the molecules. Electronegative atoms such as oxygen and nitrogen tend to form shorter, stronger hydrogen bonds due to their high electronegativity. The bond angle, which is the angle between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom, also plays a crucial role in determining the hydrogen bonding distance. A more linear bond angle typically results in a shorter hydrogen bonding distance. Additionally, the polarity of the molecules involved can influence the strength and distance of hydrogen bonds, with more polar molecules generally forming stronger, shorter hydrogen bonds.
| Atom Involved | Electronegativity | Hydrogen Bonding Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 3.44 | 1.5-2.5 |
| Nitrogen | 3.04 | 1.5-3.0 |
| Fluorine | 3.98 | 1.2-2.2 |

Impact of Hydrogen Bonding Distance on Chemical Reactions
The distance between atoms in a hydrogen bond can significantly influence the kinetics and thermodynamics of chemical reactions. Shorter hydrogen bonding distances can enhance reaction rates by increasing the proximity of reactants, while longer distances can stabilize transition states, affecting the overall reaction pathway. Furthermore, the strength of hydrogen bonds can impact the selectivity of reactions, with stronger bonds leading to more selective reactions. Recent research has highlighted the importance of considering hydrogen bonding distance in the design of catalysts and reaction conditions.
Catalytic Implications
Catalysts often rely on hydrogen bonding interactions to facilitate chemical reactions. The distance between atoms in these interactions can significantly impact the activity and selectivity of catalysts. For example, enzymes use hydrogen bonding to position substrates and stabilize transition states, with the distance between atoms playing a crucial role in determining the efficiency and specificity of enzymatic reactions. Similarly, synthetic catalysts can be designed to exploit hydrogen bonding interactions, with careful control over the distance between atoms allowing for the optimization of reaction conditions.
- Enzymatic reactions: Hydrogen bonding distance influences the positioning of substrates and the stabilization of transition states.
- Synthetic catalysts: Control over hydrogen bonding distance allows for the optimization of reaction conditions and the design of more efficient catalysts.
- Catalyst selectivity: Hydrogen bonding distance impacts the selectivity of reactions, with stronger bonds leading to more selective reactions.
How does hydrogen bonding distance affect the strength of hydrogen bonds?
+The strength of hydrogen bonds is inversely proportional to the distance between the atoms involved. Shorter distances result in stronger hydrogen bonds, while longer distances lead to weaker interactions.
What role do hydrogen bonding interactions play in enzymatic reactions?
+Hydrogen bonding interactions are crucial in enzymatic reactions, as they help position substrates and stabilize transition states. The distance between atoms in these interactions significantly influences the efficiency and specificity of enzymatic reactions.
In conclusion, the distance between atoms involved in hydrogen bonding plays a significant role in determining the strength and nature of these interactions, ultimately influencing chemical reactions. Recent research has highlighted the importance of considering hydrogen bonding distance in the design of catalysts and reaction conditions. As our understanding of hydrogen bonding continues to evolve, it is likely that new strategies for controlling and exploiting these interactions will emerge, leading to significant advances in various fields, including catalysis, materials science, and drug development.
