How To Determine H Bond Distance With Accuracy And Precision Quickly

The determination of hydrogen bond distance with accuracy and precision is crucial in understanding the structural and functional properties of molecules, particularly in the fields of biochemistry, chemistry, and pharmacology. Hydrogen bonds are weak electrostatic attractions between a hydrogen atom, which is covalently bonded to a more electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine), and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons. The strength and nature of these bonds significantly influence the stability, conformation, and reactivity of molecules.
Understanding Hydrogen Bonding
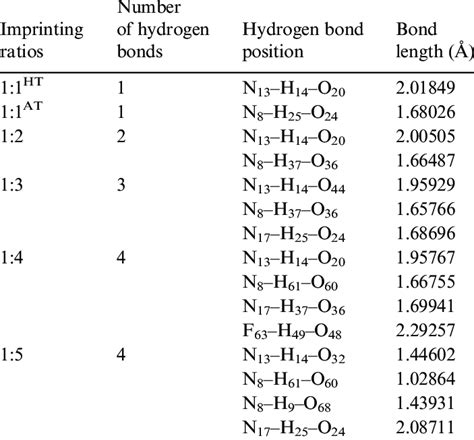
Before diving into the methods for determining hydrogen bond distances, it’s essential to understand the principles of hydrogen bonding. The distance between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom it is bonded to (D-H) and the distance between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom it is attracted to (H…A) are critical parameters. Typically, the D-H…A angle also plays a significant role in the strength of the hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are generally classified based on their strength, which correlates with the bond distance; stronger bonds have shorter distances.
Methods for Determining Hydrogen Bond Distance
Several methods can be employed to determine hydrogen bond distances with varying degrees of accuracy and precision. These include:
- X-ray Crystallography: This is one of the most direct methods for determining the three-dimensional structure of molecules, including the distances between atoms involved in hydrogen bonding. X-ray crystallography can provide highly accurate information but requires the molecule to be crystallized.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: NMR spectroscopy can provide detailed information about the molecular structure in solution. While it does not directly measure distances, it can infer them through the analysis of nuclear Overhauser effects (NOEs) and scalar coupling constants. NMR is particularly useful for studying molecules in their natural, solvated state.
- Molecular Dynamics Simulations: These computational methods simulate the behavior of molecules over time, allowing for the calculation of average distances between atoms, including those involved in hydrogen bonds. The accuracy of molecular dynamics simulations depends on the force field used and the simulation conditions.
- Neutron Scattering: Similar to X-ray scattering, neutron scattering can be used to determine structural information about molecules. It is particularly useful for locating hydrogen atoms, which are difficult to detect with X-ray methods due to their low electron density.
Each of these methods has its advantages and limitations. X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy are considered gold standards for structural biology but require specialized equipment and expertise. Molecular dynamics simulations offer a versatile and relatively accessible method for predicting hydrogen bond distances, provided that the computational resources and appropriate force fields are available.
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Crystallography | High | High | Crystallized sample, synchrotron or X-ray source |
| NMR Spectroscopy | High | High | Pure sample, NMR spectrometer |
| Molecular Dynamics Simulations | Medium to High | Medium to High | Computational resources, appropriate force field |
| Neutron Scattering | High | High | Neutron source, specialized instrumentation |
Challenges and Future Directions

Determining hydrogen bond distances with accuracy and precision can be challenging, especially in complex biological systems or when dealing with transient or weak interactions. Advances in computational power, improvements in force fields for molecular dynamics simulations, and the development of new experimental techniques are continually enhancing our ability to study hydrogen bonding.
Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) simulations and ab initio molecular dynamics are emerging as powerful tools for accurately predicting the behavior of molecules, including the formation and breaking of hydrogen bonds at the atomic level. These methods can provide detailed insights into the electronic structure and dynamics of hydrogen-bonded systems, offering a promising avenue for future research.
Implications for Drug Design and Materials Science
The accurate determination of hydrogen bond distances is crucial for understanding the mechanisms of drug action and for the design of new pharmaceuticals. Hydrogen bonds play a significant role in the recognition and binding of drugs to their targets, and precise structural information can guide the optimization of drug candidates. Similarly, in materials science, controlling hydrogen bonding is essential for designing materials with specific properties, such as supramolecular assemblies and nanostructured materials.
What is the typical distance range for hydrogen bonds?
+Hydrogen bond distances can vary, but typically, the distance between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom it is attracted to (H...A) ranges from about 1.5 to 3.0 Å, with the angle and the environment influencing the bond strength.
How do solvent effects influence hydrogen bond distances?
+Solvent effects can significantly influence hydrogen bond distances and strengths. Polar solvents, in particular, can compete with the hydrogen bonding interactions, potentially weakening or altering the bonds. The choice of solvent can thus affect the observed hydrogen bond distances in experimental and computational studies.
In conclusion, determining hydrogen bond distances with accuracy and precision is a multifaceted challenge that requires a combination of experimental and computational approaches. As our understanding of hydrogen bonding and its role in molecular interactions deepens, so too will our ability to design and engineer molecules and materials with specific properties, leading to advancements in fields from drug discovery to materials science.



