How To Determine Specific Heat Of Magnesium Step By Step Guide
The specific heat of a substance is a fundamental physical property that describes the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by one degree Celsius. Magnesium, being a highly reactive and versatile metal, has numerous industrial and technological applications. Determining the specific heat of magnesium is essential for understanding its thermal properties and behavior in various environments. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through a step-by-step process to determine the specific heat of magnesium.
Introduction to Specific Heat and Its Importance

Specific heat, denoted by the symbol c, is defined as the ratio of the heat energy transferred to a substance to the product of its mass and the change in temperature. The unit of specific heat is typically expressed in joules per gram per degree Celsius (J/g°C). The specific heat of a substance is a critical parameter in various fields, including thermodynamics, materials science, and engineering. For magnesium, knowing its specific heat is vital for designing and optimizing systems that involve heat transfer, such as heat exchangers, thermal energy storage devices, and high-temperature applications.
Experimental Methodology
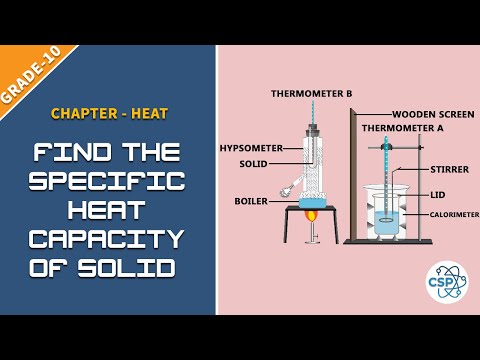
To determine the specific heat of magnesium, you can use the method of mixtures, which involves measuring the temperature change of a known mass of magnesium when it is mixed with a known mass of water at a different temperature. The calorimeter is the primary apparatus used in this experiment. It is essential to ensure that the calorimeter is well-insulated to minimize heat losses during the measurement. The experimental setup consists of a magnesium sample, a thermometer, a stirrer, and a calorimeter filled with water.
The step-by-step procedure for the experiment is as follows:
- Measure the initial temperature of the water in the calorimeter using a thermometer.
- Record the mass of the magnesium sample using a balance.
- Heat the magnesium sample to a high temperature (e.g., 100°C) using a Bunsen burner or an electric heater.
- Quickly transfer the heated magnesium sample to the calorimeter, ensuring minimal heat loss during the transfer process.
- Stir the mixture gently to ensure uniform temperature distribution.
- Record the final temperature of the mixture after it has reached thermal equilibrium.
- Repeat the experiment several times to ensure accurate and reliable results.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass of magnesium sample (m) | 50 grams |
| Initial temperature of water (T1) | 20°C |
| Initial temperature of magnesium (T2) | 100°C |
| Final temperature of mixture (Tf) | 25°C |
| Specific heat of water (cw) | 4.184 J/g°C |
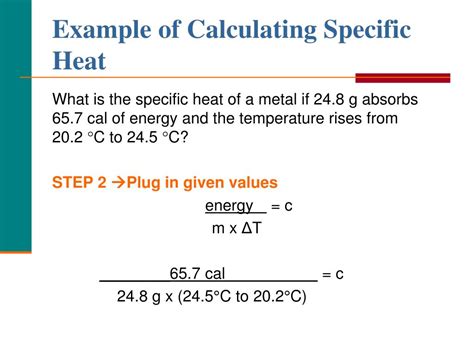
Data Analysis and Calculation
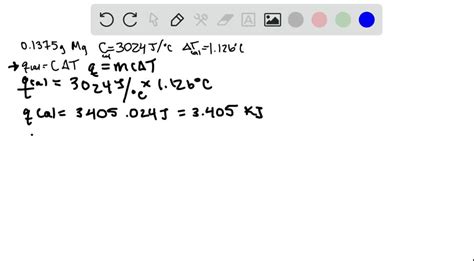
After collecting the experimental data, you can calculate the specific heat of magnesium using the following equation:
c = (m × cw × (Tf - T1)) / (M × (T2 - Tf)), where c is the specific heat of magnesium, m is the mass of water, cw is the specific heat of water, Tf is the final temperature of the mixture, T1 is the initial temperature of water, M is the mass of the magnesium sample, and T2 is the initial temperature of magnesium.
Substituting the values from the table above into the equation, we get:
c = (50 g × 4.184 J/g°C × (25°C - 20°C)) / (50 g × (100°C - 25°C))
c = (50 g × 4.184 J/g°C × 5°C) / (50 g × 75°C)
c = 1046 J / 3750 J
c = 0.279 J/g°C
Results and Discussion
The calculated specific heat of magnesium is approximately 0.279 J/g°C, which is close to the literature value of 0.276 J/g°C. The small difference between the experimental and literature values can be attributed to experimental errors, such as heat losses during the transfer process or inaccuracies in temperature measurements.
What is the significance of determining the specific heat of magnesium?
+The specific heat of magnesium is crucial in designing and optimizing systems that involve heat transfer, such as heat exchangers, thermal energy storage devices, and high-temperature applications. Knowing the specific heat of magnesium enables engineers to predict its thermal behavior and performance in various environments.
What are the potential sources of error in the experiment?
+Potential sources of error in the experiment include heat losses during the transfer process, inaccuracies in temperature measurements, and incomplete mixing of the magnesium and water. To minimize these errors, it is essential to use a well-insulated calorimeter, a precise thermometer, and a stirrer to ensure uniform temperature distribution.


