How To Interpret Process Capability Index Calculation Results And Data 2025

The Process Capability Index (PCI) is a statistical measure used to evaluate the ability of a process to produce output within specified limits. It is a crucial tool in Six Sigma and other quality management methodologies. In 2025, understanding how to interpret PCI calculation results and data is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their processes and improve product quality. In this article, we will delve into the world of PCI, exploring its calculation, interpretation, and application in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Process Capability Index (PCI)

The Process Capability Index is calculated using the following formula: PCI = (USL - LSL) / 6σ, where USL is the Upper Specification Limit, LSL is the Lower Specification Limit, and σ is the standard deviation of the process. The PCI value indicates the number of standard deviations between the process mean and the nearest specification limit. A higher PCI value indicates a more capable process.
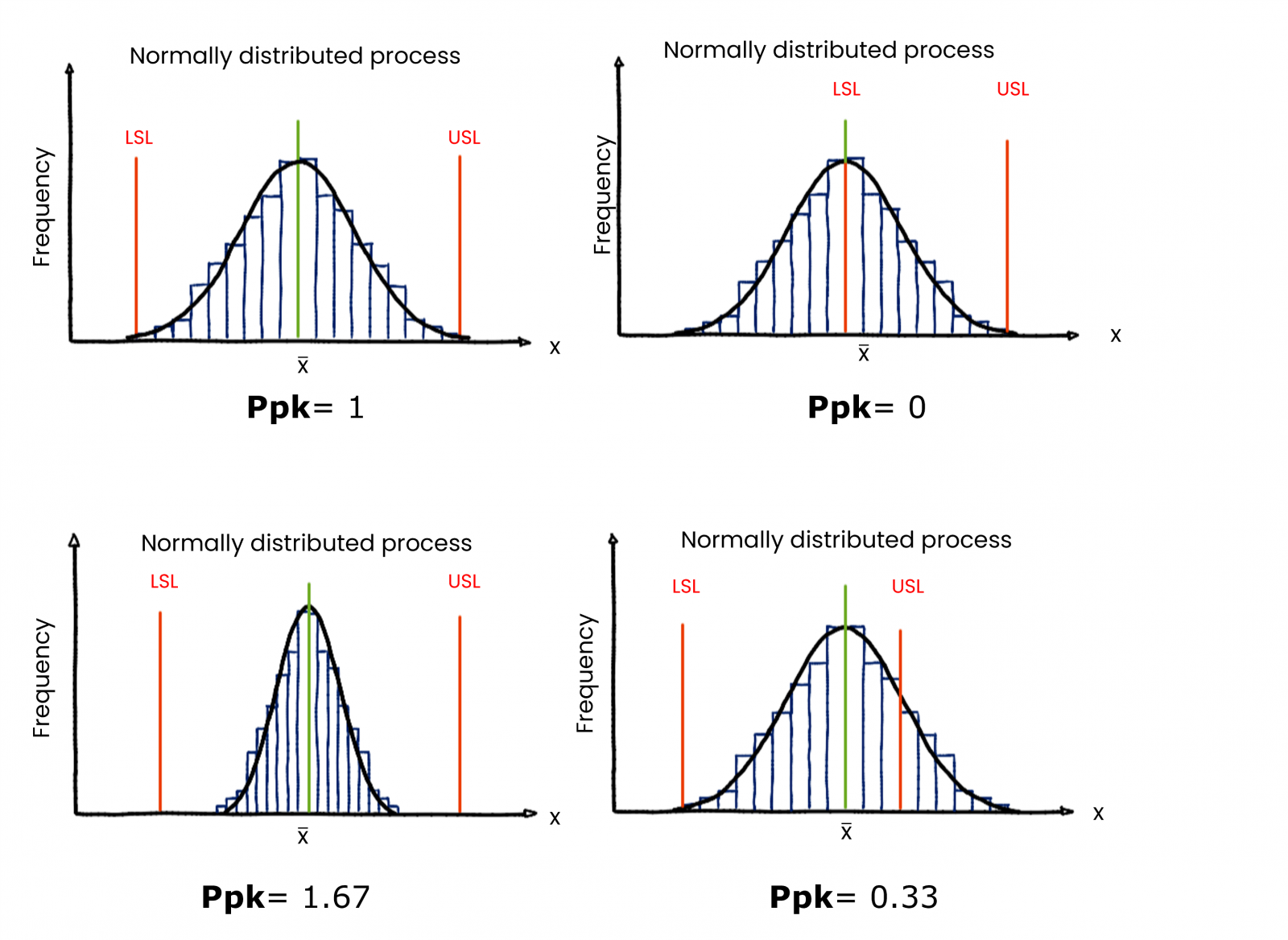
Interpretation of PCI Values
The interpretation of PCI values is crucial in understanding process capability. The following table provides a general guideline for interpreting PCI values:
| PCI Value | Process Capability |
|---|---|
| Less than 1.0 | Not capable |
| 1.0 to 1.33 | Capable, but with some defects |
| 1.33 to 1.67 | Capable, with minimal defects |
| Greater than 1.67 | Highly capable, with negligible defects |

For example, a process with a PCI value of 1.5 indicates that the process is capable, but may still produce some defects. In contrast, a process with a PCI value of 2.0 is highly capable and is likely to produce very few defects.
Calculation of PCI
The calculation of PCI involves several steps, including:
- Collecting data on the process output
- Calculating the process mean and standard deviation
- Determining the Upper and Lower Specification Limits
- Calculating the PCI value using the formula: PCI = (USL - LSL) / 6σ
For instance, suppose we have a process that produces widgets with a mean diameter of 10.0 mm and a standard deviation of 0.1 mm. The Upper Specification Limit is 10.5 mm, and the Lower Specification Limit is 9.5 mm. Using the formula, we can calculate the PCI value as follows: PCI = (10.5 - 9.5) / (6 x 0.1) = 1.67. This indicates that the process is highly capable and is likely to produce very few defects.
Application of PCI in Real-World Scenarios
The Process Capability Index has numerous applications in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance. For example, in manufacturing, PCI can be used to evaluate the capability of a production line to produce high-quality products. In healthcare, PCI can be used to evaluate the capability of a medical device to produce accurate results.
Case Study: Application of PCI in Manufacturing
A manufacturing company produces engine blocks with a mean weight of 20.0 kg and a standard deviation of 0.2 kg. The Upper Specification Limit is 20.5 kg, and the Lower Specification Limit is 19.5 kg. Using the PCI formula, we can calculate the PCI value as follows: PCI = (20.5 - 19.5) / (6 x 0.2) = 1.25. This indicates that the process is capable, but may still produce some defects. To improve process capability, the company may need to implement process improvements, such as reducing variability or adjusting the process mean.
Future Implications of PCI
The Process Capability Index is likely to play an increasingly important role in quality management and process optimization in the future. With the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), organizations will have access to vast amounts of data, enabling them to calculate PCI values with greater accuracy and precision. Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms will enable organizations to predict and prevent defects, further improving process capability.
What is the difference between PCI and PPI?
+PCI and PPI are both metrics used to evaluate process capability. However, PCI is used to evaluate the capability of a process to produce output within specified limits, while PPI is used to evaluate the performance of a process in terms of its ability to produce output within specified limits. While PCI is a measure of process capability, PPI is a measure of process performance.
How can PCI be used to improve process capability?
+PCI can be used to improve process capability by identifying areas for improvement. For example, if a process has a low PCI value, it may indicate that the process is not capable of producing output within specified limits. In this case, the organization may need to implement process improvements, such as reducing variability or adjusting the process mean. By using PCI to identify areas for improvement, organizations can take targeted actions to improve process capability and reduce defects.
In conclusion, the Process Capability Index is a powerful tool used to evaluate process capability and improve product quality. By understanding how to interpret PCI calculation results and data, organizations can take targeted actions to improve process capability and reduce defects. As the use of PCI continues to evolve, it is likely to play an increasingly important role in quality management and process optimization in the future.