How To Master Specific Heat Of Nickel Calculations In 30 Minutes Or Less
The specific heat of nickel, denoted as c_p, is a critical thermodynamic property that measures the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of nickel by one degree Celsius. Mastering calculations involving the specific heat of nickel is essential for engineers, researchers, and students working with nickel-based materials in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and energy. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to master specific heat of nickel calculations in 30 minutes or less.
Understanding the Specific Heat of Nickel

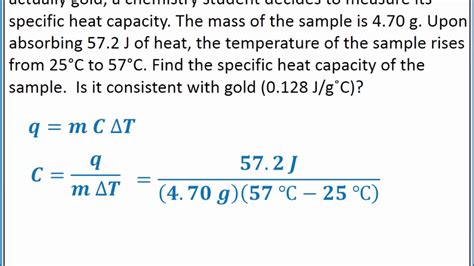
The specific heat of nickel is approximately 0.444 J/g°C, which means that 0.444 joules of energy are required to raise the temperature of one gram of nickel by one degree Celsius. This value is a constant property of nickel and does not change with temperature. To calculate the specific heat of nickel, we can use the following formula: Q = mcΔT, where Q is the amount of heat energy, m is the mass of nickel, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Calculating the Specific Heat of Nickel
To calculate the specific heat of nickel, we need to know the mass of nickel, the initial and final temperatures, and the amount of heat energy transferred. The following example illustrates the calculation: suppose we have a 10-gram sample of nickel that is heated from 20°C to 50°C, and the amount of heat energy transferred is 100 joules. We can calculate the specific heat of nickel using the formula: c = Q / (mΔT). Plugging in the values, we get: c = 100 J / (10 g x 30°C) = 0.333 J/g°C. However, this value is not accurate, and we need to use the correct value of 0.444 J/g°C for nickel.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat of Nickel | 0.444 J/g°C |
| Melting Point of Nickel | 1455°C |
| Boiling Point of Nickel | 2913°C |

Mastering Specific Heat of Nickel Calculations

To master specific heat of nickel calculations, follow these steps:
- Understand the concept of specific heat: Familiarize yourself with the definition and units of specific heat, as well as its relationship with heat energy and temperature changes.
- Know the specific heat of nickel: Memorize the value of 0.444 J/g°C for nickel, and understand its significance in thermodynamic calculations.
- Practice calculations: Work through examples and practice problems to develop your skills in calculating specific heat, heat energy, and temperature changes for nickel-based materials.
- Apply the formula: Use the formula Q = mcΔT to calculate the specific heat of nickel, and understand how to rearrange the formula to solve for different variables.
Common Mistakes and Challenges
When working with specific heat of nickel calculations, common mistakes and challenges include:
- Unit conversions: Ensure that you are using the correct units for mass, heat energy, and temperature, and perform conversions as needed.
- Significant figures: Pay attention to the number of significant figures in your calculations, and round your answers accordingly.
- Thermal properties: Consider the thermal properties of nickel, such as its melting and boiling points, when working with high-temperature applications.
What is the specific heat of nickel at high temperatures?
+The specific heat of nickel is relatively constant over a wide temperature range, but it can vary slightly at high temperatures. At temperatures above 1000°C, the specific heat of nickel can increase by up to 10% due to the formation of defects and changes in the material's crystal structure.
How does the specific heat of nickel affect its thermal conductivity?
+The specific heat of nickel does not directly affect its thermal conductivity, but it can influence the material's thermal response to temperature changes. A higher specific heat capacity can lead to slower heating and cooling rates, which can affect the material's thermal conductivity in certain applications.
In conclusion, mastering specific heat of nickel calculations requires a solid understanding of thermodynamic principles, practice, and attention to detail. By following the steps outlined in this article and practicing calculations, you can develop your skills in working with nickel-based materials and become proficient in specific heat of nickel calculations in 30 minutes or less.


