How To Optimize Cellulose Insulation R Value For Cold Climates In 2025
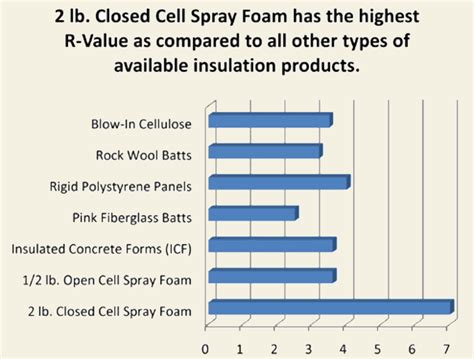
Cellulose insulation has been a popular choice for building owners in cold climates due to its high R-value, which measures the material's ability to resist heat flow. As of 2025, optimizing cellulose insulation R-value is crucial to achieve maximum energy efficiency and minimize heat loss in cold climates. The R-value of cellulose insulation depends on various factors, including its density, moisture content, and installation method. In this article, we will discuss the factors that affect cellulose insulation R-value and provide tips on how to optimize it for cold climates.
Understanding Cellulose Insulation R-Value

Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper products, such as newspaper and cardboard, which are treated with fire retardants and other additives. The R-value of cellulose insulation varies depending on its density, which ranges from 1.5 to 3.5 pounds per cubic foot. The higher the density, the higher the R-value. For example, a density of 2.5 pounds per cubic foot can achieve an R-value of around R-3.8 per inch, while a density of 3.5 pounds per cubic foot can achieve an R-value of around R-4.2 per inch.
Factors Affecting Cellulose Insulation R-Value
Several factors can affect the R-value of cellulose insulation, including:
- Density: As mentioned earlier, the density of cellulose insulation is a critical factor in determining its R-value. Higher density insulation generally has a higher R-value.
- Moisture content: Cellulose insulation is sensitive to moisture, which can reduce its R-value. It is essential to ensure that the insulation is dry and free of moisture during installation.
- Installation method: The installation method can also affect the R-value of cellulose insulation. Proper installation, including filling all gaps and voids, is crucial to achieve maximum R-value.
- Aging: Cellulose insulation can settle over time, which can reduce its R-value. However, this effect can be minimized by using a high-density insulation and ensuring proper installation.
| Density (lbs/ft³) | R-Value (per inch) |
|---|---|
| 1.5 | R-3.2 |
| 2.0 | R-3.5 |
| 2.5 | R-3.8 |
| 3.0 | R-4.1 |
| 3.5 | R-4.2 |

Optimizing Cellulose Insulation R-Value for Cold Climates

To optimize cellulose insulation R-value for cold climates, consider the following tips:
- Use high-density insulation: High-density insulation has a higher R-value, making it ideal for cold climates.
- Ensure proper installation: Proper installation, including filling all gaps and voids, is crucial to achieve maximum R-value.
- Minimize moisture content: Cellulose insulation is sensitive to moisture, which can reduce its R-value. Ensure that the insulation is dry and free of moisture during installation.
- Use a vapor barrier: A vapor barrier can help reduce moisture infiltration and maintain the insulation’s R-value.
- Consider radiant barrier insulation: Radiant barrier insulation can help reflect heat rather than absorb it, reducing heat loss and improving the overall R-value of the insulation.
Cold Climate Considerations
Cold climates present unique challenges for cellulose insulation, including:
- Cold temperatures: Cold temperatures can reduce the R-value of cellulose insulation. However, high-density insulation can help minimize this effect.
- Moisture: Cold climates often experience high levels of moisture, which can reduce the R-value of cellulose insulation. Ensure that the insulation is dry and free of moisture during installation.
- Wind-driven rain: Wind-driven rain can infiltrate the insulation, reducing its R-value. Use a vapor barrier to minimize moisture infiltration.
What is the recommended density for cellulose insulation in cold climates?
+The recommended density for cellulose insulation in cold climates is at least 2.5 pounds per cubic foot to achieve a high R-value.
How can I minimize moisture content in cellulose insulation?
+To minimize moisture content in cellulose insulation, ensure that the insulation is dry and free of moisture during installation. Use a vapor barrier to reduce moisture infiltration, and consider using a dehumidifier to maintain a dry environment.
In conclusion, optimizing cellulose insulation R-value for cold climates requires careful consideration of various factors, including density, moisture content, and installation method. By using high-density insulation, ensuring proper installation, and minimizing moisture content, building owners can achieve maximum energy efficiency and reduce heat loss in cold climates. Additionally, considering radiant barrier insulation and using a vapor barrier can further improve the overall R-value of the insulation.


