How To Use Capability Index Calculation For Improved Product Quality Control Always
The capability index calculation is a statistical tool used in quality control to measure the ability of a process to produce output within specified limits. It is an essential metric for evaluating the performance of manufacturing processes and ensuring that products meet customer requirements. In this article, we will discuss how to use capability index calculation for improved product quality control, including the different types of capability indices, their calculation formulas, and practical applications.
Understanding Capability Indices
Capability indices are dimensionless numbers that compare the spread of a process with the specification limits. The most commonly used capability indices are:
- Cp (Capability Index): measures the potential capability of a process
- Cpk (Centered Capability Index): measures the actual capability of a process, taking into account the centering of the process mean
- Cpm (Modified Capability Index): measures the capability of a process, taking into account the variability of the process mean
These indices provide a quantitative measure of the process capability, allowing quality control engineers to identify areas for improvement and optimize processes to produce high-quality products.
Calculating Capability Indices
The calculation formulas for capability indices are as follows:
| Capability Index | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|
| Cp | Cp = (USL - LSL) / (6 * σ) |
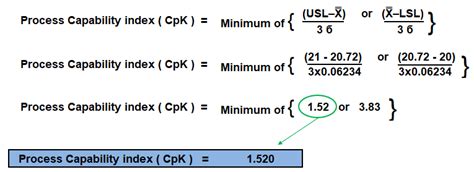
| Cpk | Cpk = min[(USL - μ) / (3 * σ), (μ - LSL) / (3 * σ)] |
| Cpm | Cpm = (USL - LSL) / (6 * σ_m) |

where USL is the upper specification limit, LSL is the lower specification limit, μ is the process mean, σ is the standard deviation of the process, and σ_m is the modified standard deviation.
Interpreting Capability Indices
The interpretation of capability indices is as follows:
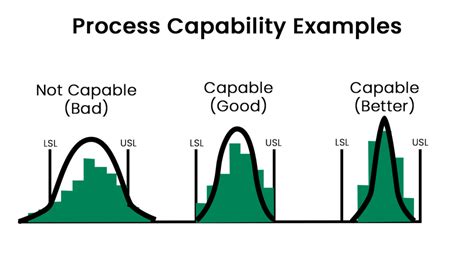
- Cp > 1: the process is capable of producing output within the specified limits
- Cp = 1: the process is barely capable of producing output within the specified limits
- Cp < 1: the process is not capable of producing output within the specified limits
- Cpk > 1.33: the process is centered and capable of producing output within the specified limits
- Cpk = 1.33: the process is barely centered and capable of producing output within the specified limits
- Cpk < 1.33: the process is not centered or capable of producing output within the specified limits
By understanding the capability indices and their interpretation, quality control engineers can identify areas for improvement and optimize processes to produce high-quality products.
Practical Applications of Capability Index Calculation

Capability index calculation has numerous practical applications in quality control, including:
- Process optimization: capability indices can be used to identify areas for improvement in a process and optimize it to produce high-quality products
- Specification setting: capability indices can be used to set realistic specification limits for a process
- Supplier selection: capability indices can be used to evaluate the capability of suppliers and select those that can produce high-quality products
- Product development: capability indices can be used to evaluate the capability of new products and processes during the development phase
By applying capability index calculation in these areas, organizations can improve product quality, reduce defects, and increase customer satisfaction.
Real-World Example
A manufacturing company produces engine blocks with a specification limit of 10.0 ± 0.5 mm. The process mean is 10.2 mm, and the standard deviation is 0.1 mm. To calculate the capability indices, we can use the following formulas:
| Capability Index | Calculation Formula | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cp | Cp = (USL - LSL) / (6 * σ) | Cp = (10.5 - 9.5) / (6 * 0.1) = 1.67 |
| Cpk | Cpk = min[(USL - μ) / (3 * σ), (μ - LSL) / (3 * σ)] | Cpk = min[(10.5 - 10.2) / (3 * 0.1), (10.2 - 9.5) / (3 * 0.1)] = 1.33 |
Based on the calculation, the process is capable of producing engine blocks within the specified limits, and the process mean is centered. However, the Cpk value indicates that the process is barely capable of producing output within the specified limits, and further optimization is required to improve the process capability.
What is the purpose of capability index calculation in quality control?
+The purpose of capability index calculation is to measure the ability of a process to produce output within specified limits, allowing quality control engineers to identify areas for improvement and optimize processes to produce high-quality products.
How do I calculate the capability indices for a process?
+The calculation formulas for capability indices are as follows: Cp = (USL - LSL) / (6 * σ), Cpk = min[(USL - μ) / (3 * σ), (μ - LSL) / (3 * σ)], and Cpm = (USL - LSL) / (6 * σ_m), where USL is the upper specification limit, LSL is the lower specification limit, μ is the process mean, σ is the standard deviation of the process, and σ_m is the modified standard deviation.
What is the difference between Cp, Cpk, and Cpm?
+Cp measures the potential capability of a process, Cpk measures the actual capability of a process, taking into account the centering of the process mean, and Cpm measures the capability of a process, taking into account the variability of the process mean.



