Mercury Specific Heat

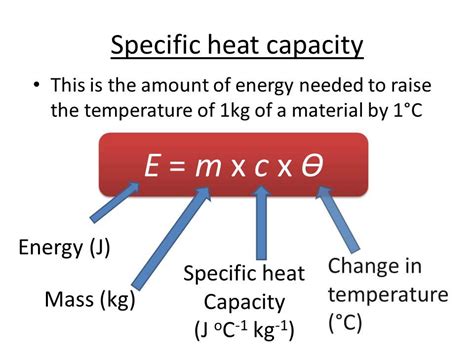
The specific heat capacity of a substance is a measure of the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by one degree Celsius. Mercury, being a metal with unique properties, has a specific heat capacity that is of interest in various scientific and industrial applications. The specific heat capacity of mercury is approximately 0.138 J/g°C, which is relatively low compared to other metals.
Properties of Mercury
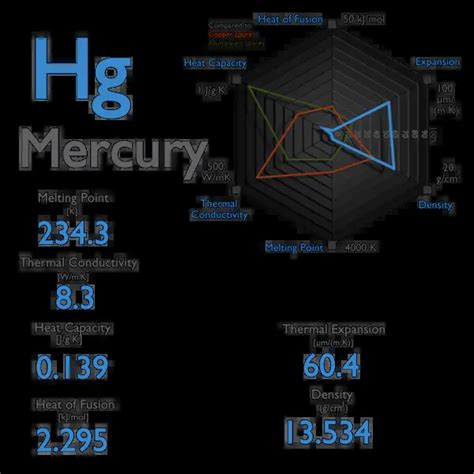
Mercury is a dense, silvery-white metal that is liquid at room temperature. Its unique properties, such as its high density and low melting point, make it an interesting subject for study. The specific heat capacity of mercury is an important property that determines its thermal behavior. The low specific heat capacity of mercury means that it can absorb and release heat energy quickly, making it useful in applications where rapid temperature changes are required.
Factors Affecting Specific Heat Capacity
The specific heat capacity of mercury can be affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and purity. The specific heat capacity of mercury increases with temperature, which means that more heat energy is required to raise the temperature of mercury at higher temperatures. The pressure dependence of the specific heat capacity of mercury is relatively small, but it can still have a significant effect at very high pressures. The purity of mercury can also affect its specific heat capacity, as impurities can alter the thermal properties of the metal.
| Temperature (°C) | Specific Heat Capacity (J/g°C) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 0.138 |
| 50 | 0.140 |
| 100 | 0.142 |

Applications of Mercury
Mercury has several industrial and scientific applications, including thermometers, barometers, and fluorescent lighting. The low specific heat capacity of mercury makes it useful in applications where rapid temperature changes are required. For example, in thermometers, mercury is used as a working fluid because it can expand and contract quickly in response to temperature changes. In fluorescent lighting, mercury is used as a vapor to create ultraviolet light, which is then converted to visible light by a phosphor coating.
Thermal Energy Storage
The specific heat capacity of mercury makes it a potential material for thermal energy storage applications. Thermal energy storage systems store heat energy during off-peak hours and release it during peak hours, reducing the strain on the power grid. Mercury’s low specific heat capacity means that it can absorb and release heat energy quickly, making it useful for rapid charging and discharging cycles.
- Mercury has a high density, which makes it useful for applications where space is limited.
- The low specific heat capacity of mercury means that it can absorb and release heat energy quickly.
- Mercury is a toxic substance and requires special handling and disposal procedures.
What is the specific heat capacity of mercury?
+The specific heat capacity of mercury is approximately 0.138 J/g°C.
What factors affect the specific heat capacity of mercury?
+The specific heat capacity of mercury can be affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and purity.
What are some applications of mercury?
+Mercury has several industrial and scientific applications, including thermometers, barometers, and fluorescent lighting.
In conclusion, the specific heat capacity of mercury is an important property that determines its thermal behavior. Understanding the factors that affect the specific heat capacity of mercury is crucial for optimizing its performance in various applications. The low specific heat capacity of mercury makes it useful in applications where rapid temperature changes are required, such as thermometers and thermal energy storage systems.