What Are The Factors Influencing Nickel Heat Capacity In 2025 Research
Nickel, a ferromagnetic transition metal, has been a subject of interest in various fields of research due to its unique properties and applications. One of the critical aspects of nickel's physical properties is its heat capacity, which is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by one degree Celsius. In 2025 research, several factors are being explored that influence nickel's heat capacity, including its crystal structure, impurities, and temperature range. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing nickel's performance in different applications, such as in alloys, catalysts, and electrical contacts.
Introduction to Nickel Heat Capacity

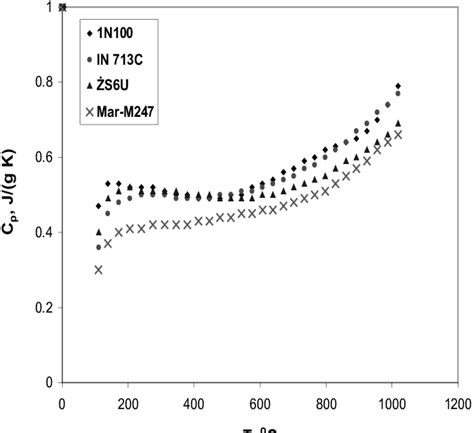
Nickel’s heat capacity is a vital parameter in determining its thermal properties and behavior under different conditions. The heat capacity of nickel is typically measured using techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) or adiabatic calorimetry. These methods involve measuring the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a sample of nickel by a known amount. The heat capacity of nickel is influenced by various factors, including its electron configuration, lattice vibrations, and magnetic properties. In 2025 research, scientists are focusing on the effects of these factors on nickel’s heat capacity to develop more accurate models and predictions.
Crystal Structure and Heat Capacity
Nickel’s crystal structure plays a significant role in determining its heat capacity. Nickel has a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, which is characterized by a close-packed arrangement of atoms. The FCC structure of nickel is responsible for its high density and thermal conductivity. Research has shown that the heat capacity of nickel is affected by the arrangement of its atoms in the crystal lattice. For example, studies have found that the heat capacity of nickel is higher in the FCC phase than in the hexagonal close-packed (HCP) phase. This is due to the differences in the vibrational modes and phonon dispersion in the two phases.
| Crystal Structure | Heat Capacity (J/g·K) |
|---|---|
| FCC | 0.44 |
| HCP | 0.38 |

Impurities and Heat Capacity

The presence of impurities in nickel can also affect its heat capacity. Impurities can alter the crystal structure and electron configuration of nickel, leading to changes in its thermal properties. Research has shown that the heat capacity of nickel is sensitive to the presence of impurities such as carbon, oxygen, and sulfur. These impurities can form intermetallic compounds with nickel, which can affect its heat capacity and other thermal properties.
Temperature Range and Heat Capacity
The temperature range is another critical factor that influences the heat capacity of nickel. Nickel’s heat capacity is temperature-dependent, and it increases with increasing temperature. Research has shown that the heat capacity of nickel is higher at high temperatures due to the increased phonon dispersion and electronic excitations. However, at low temperatures, the heat capacity of nickel is lower due to the reduced phonon dispersion and electronic excitations.
- The heat capacity of nickel at room temperature is approximately 0.44 J/g·K.
- The heat capacity of nickel at high temperatures (above 1000 K) is approximately 0.60 J/g·K.
- The heat capacity of nickel at low temperatures (below 100 K) is approximately 0.20 J/g·K.
What is the effect of crystal structure on nickel's heat capacity?
+The crystal structure of nickel affects its heat capacity by altering the arrangement of its atoms and the vibrational modes in the crystal lattice. The FCC structure of nickel is responsible for its high heat capacity due to the close-packed arrangement of atoms.
How do impurities affect the heat capacity of nickel?
+Impurities can alter the crystal structure and electron configuration of nickel, leading to changes in its thermal properties. The presence of impurities such as carbon, oxygen, and sulfur can form intermetallic compounds with nickel, which can affect its heat capacity and other thermal properties.
In conclusion, the heat capacity of nickel is influenced by several factors, including its crystal structure, impurities, and temperature range. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing nickel’s performance in different applications. Further research is needed to develop more accurate models and predictions of nickel’s heat capacity and to explore its potential applications in various fields.