What Are The Key Considerations For Nickel Heat Capacity In 2025 Engineering Designs
Nickel, a versatile and widely used metal, plays a crucial role in various engineering applications due to its unique properties, including its heat capacity. As we move into 2025, understanding the key considerations for nickel heat capacity in engineering designs is essential for optimizing performance, safety, and efficiency in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, and energy production. The heat capacity of a material, which is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the material by one degree Celsius, is a critical factor in designing systems that involve heat transfer, thermal management, and energy storage.
Introduction to Nickel and Its Properties

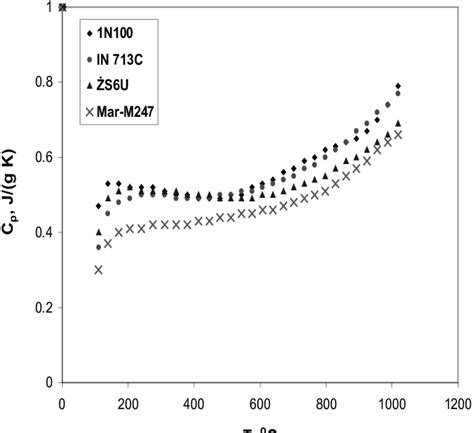
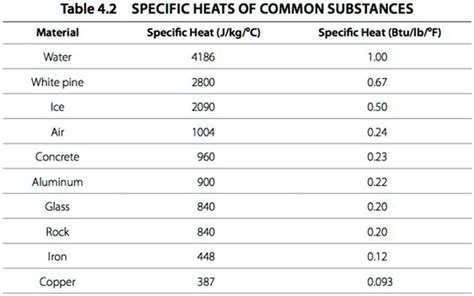
Nickel, with an atomic number of 28, is a ferromagnetic metal that exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, high ductility, and a relatively high melting point of about 1455°C. Its thermal conductivity is approximately 90.9 W/m-K, which is significant for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. Nickel’s specific heat capacity at 20°C is around 0.509 J/g°C, which means it can absorb a considerable amount of heat energy without a significant rise in temperature, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Nickel Alloys and Their Heat Capacity
In engineering designs, pure nickel is often alloyed with other elements to enhance its properties. These alloys, such as Inconel (a nickel-chromium alloy) and Monel (a nickel-copper alloy), have different heat capacities compared to pure nickel. For instance, Inconel 600 has a specific heat capacity of approximately 0.435 J/g°C at 20°C, which is lower than that of pure nickel but still offers excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it ideal for use in nuclear reactors and heat exchangers. Understanding the heat capacity of these alloys is crucial for designing components that will be exposed to high temperatures and for predicting their thermal behavior.
| Nickel Alloy | Specific Heat Capacity (J/g°C) |
|---|---|
| Pure Nickel | 0.509 |
| Inconel 600 | 0.435 |
| Monel 400 | 0.456 |

Applications and Considerations
In 2025 engineering designs, nickel and its alloys are anticipated to play pivotal roles in various applications, including renewable energy systems, aerospace engineering, and advanced manufacturing. For instance, in the development of heat exchangers for solar thermal systems, the heat capacity of nickel alloys can influence the system’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Similarly, in turbine blades for gas turbines, the ability of nickel alloys to withstand high temperatures and stresses is critical, and their heat capacity affects the blade’s thermal management and overall performance.
Thermal Management and Efficiency
Effective thermal management is key to enhancing the efficiency and lifespan of systems that involve high temperatures. The heat capacity of nickel and its alloys must be carefully considered to ensure that components can absorb and dissipate heat as required. This involves not just the selection of appropriate materials but also the design of the system’s geometry and the integration of cooling systems. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA) are invaluable tools in this context, allowing engineers to simulate and predict the thermal behavior of components and systems.
Furthermore, the recyclability of nickel and its alloys is an increasingly important consideration, given the push towards more sustainable engineering practices. Nickel alloys can be recycled, which not only conserves natural resources but also reduces the energy required for producing new materials, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This aspect highlights the need for a holistic approach to material selection, considering both performance characteristics and environmental impact.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right nickel alloy based on the specific requirements of the application, including temperature range, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties.
- Thermal Design: Optimizing the design for efficient heat transfer, which may involve complex geometries and the use of advanced materials and coatings.
- Sustainability: Considering the environmental impact of material selection and system design, including recyclability, energy efficiency, and minimal waste generation.
What are the primary factors influencing the selection of nickel alloys in high-temperature applications?
+The primary factors include the alloy's melting point, thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, resistance to corrosion and oxidation, and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. Additionally, considerations such as cost, availability, and recyclability play significant roles in the decision-making process.
How does the heat capacity of nickel alloys impact the design of heat exchangers?
+The heat capacity of nickel alloys affects the heat exchanger's efficiency and size. Alloys with higher heat capacities can absorb more heat, potentially reducing the size of the heat exchanger needed for a given application. However, this must be balanced against other factors such as cost, corrosion resistance, and the alloy's thermal conductivity.
In conclusion, the heat capacity of nickel and its alloys is a critical factor in 2025 engineering designs, particularly in applications involving high temperatures. By understanding the properties of these materials and carefully considering factors such as thermal management, sustainability, and system efficiency, engineers can create innovative solutions that meet the demanding requirements of modern industries while minimizing environmental impact.



