What Is The Heat Capacity Of Nickel In 2025 Industrial Applications?

Nickel, a versatile and widely used metal in various industrial applications, exhibits specific thermal properties that are crucial for its performance and efficiency in different processes. One of the key thermal properties of nickel is its heat capacity, which is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of the substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin). Understanding the heat capacity of nickel is essential for designing and optimizing systems where nickel is used, such as in heat exchangers, catalytic converters, and high-temperature alloys.
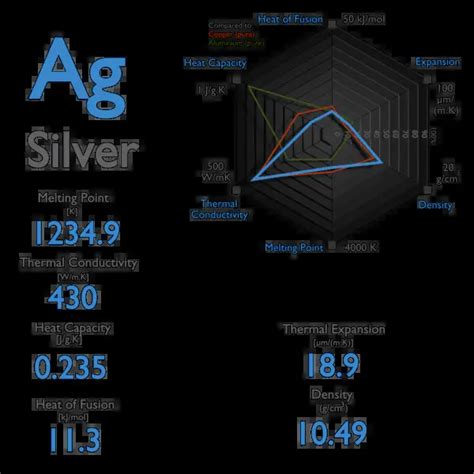
In the context of 2025 industrial applications, the heat capacity of nickel remains a critical parameter. The specific heat capacity of nickel at constant pressure is approximately 0.509 joules per gram per Kelvin (J/g·K) at room temperature. However, it's important to note that the heat capacity of nickel can vary slightly depending on its purity, the presence of impurities, and its crystalline structure. For instance, the heat capacity of pure nickel (99.99% or higher) might differ from that of nickel alloys, which are commonly used in industrial applications due to their enhanced mechanical and corrosion resistance properties.
Heat Capacity of Nickel in Different Industrial Applications

The heat capacity of nickel plays a significant role in various industrial processes. In the production of stainless steel, for example, nickel is a key alloying element that enhances corrosion resistance and durability. The heat capacity of nickel influences the thermal management of steel production processes, including melting, forging, and heat treatment. Understanding the heat capacity of nickel in these processes helps in optimizing energy consumption and ensuring the quality of the final product.
In the aerospace industry, nickel-based superalloys are used in the manufacture of turbine blades and other high-temperature components in jet engines. The heat capacity of these alloys is critical for their performance under extreme temperature conditions. A higher heat capacity can help in absorbing and dissipating heat more effectively, thus improving the component's lifespan and reliability. Researchers and engineers continually seek to develop new nickel-based alloys with optimized thermal properties, including heat capacity, for advanced aerospace applications.
Nickel Alloys and Their Heat Capacities
Nickel alloys, such as Inconel and Monel, are widely used in chemical processing, power generation, and other industries where high corrosion resistance and strength at elevated temperatures are required. The heat capacities of these alloys can vary depending on their composition. For example, Inconel 600, which contains approximately 76% nickel, has a specific heat capacity of about 0.439 J/g·K at 20°C. In contrast, Monel 400, with about 63% nickel, has a slightly higher specific heat capacity due to its different alloying elements.
| Nickel Alloy | Composition (% Nickel) | Specific Heat Capacity (J/g·K) at 20°C |
|---|---|---|
| Inconel 600 | 76 | 0.439 |
| Monel 400 | 63 | 0.452 |
| Nickel 200 | 99.5 | 0.509 |
Future Implications and Research Directions
As industrial applications continue to evolve, with increasing demands for efficiency, sustainability, and performance, the role of nickel and its alloys will remain significant. Future research directions include the development of new nickel-based materials with tailored thermal properties, including heat capacity, for advanced applications such as energy storage, thermal energy conversion, and high-temperature electronics. Additionally, the integration of nickel alloys in innovative technologies, such as 3D printing and nanotechnology, is expected to open new avenues for their application, further emphasizing the importance of understanding their thermal properties.
The advancement in computational materials science and modeling also promises to play a crucial role in predicting and optimizing the heat capacity of nickel alloys, allowing for more precise design and optimization of industrial processes and components. This interdisciplinary approach, combining materials science, thermal engineering, and computational modeling, will be essential for fully exploiting the potential of nickel and its alloys in future industrial applications.
What is the significance of heat capacity in industrial applications of nickel?
+The heat capacity of nickel is significant because it influences the thermal management and energy efficiency of various industrial processes. Understanding and optimizing the heat capacity of nickel and its alloys can lead to improved performance, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced durability of components and systems.
How does the composition of nickel alloys affect their heat capacity?
+The composition of nickel alloys, including the types and percentages of alloying elements, can significantly affect their heat capacity. Different elements contribute differently to the thermal properties of the alloy, and thus, the heat capacity can vary among different nickel alloys. The specific heat capacity is typically provided by the manufacturer or can be determined through thermal analysis.
In conclusion, the heat capacity of nickel and its alloys is a critical parameter in various industrial applications, influencing performance, efficiency, and durability. As technology advances and new applications emerge, the understanding and optimization of thermal properties, including heat capacity, will remain a focal point for research and development in the field of materials science and engineering.