Why Is Understanding Hydrogen Bonding Distance Essential For Chemists And Researchers
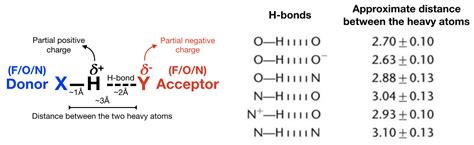
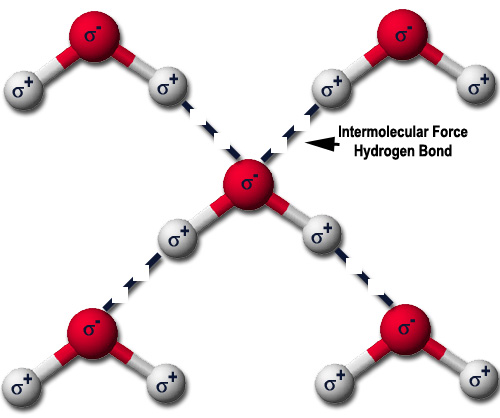
Hydrogen bonding is a fundamental concept in chemistry, playing a crucial role in the structure and properties of molecules. The distance between atoms involved in hydrogen bonding is a critical parameter that influences the strength and stability of these interactions. Understanding hydrogen bonding distance is essential for chemists and researchers, as it has significant implications for various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. In this context, the hydrogen bonding distance refers to the interatomic distance between the hydrogen atom and the atom it is bonded to, typically oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonding Distance

The hydrogen bonding distance is a key factor in determining the strength of hydrogen bonds. A shorter distance typically results in a stronger bond, while a longer distance leads to a weaker bond. This is because the electrostatic interaction between the hydrogen atom and the atom it is bonded to decreases with increasing distance. Chemists and researchers need to understand the hydrogen bonding distance to predict the stability and reactivity of molecules, design new materials, and develop new drugs. For instance, the hydrogen bonding distance in protein-ligand interactions is critical in understanding the binding affinity and specificity of proteins.
Factors Influencing Hydrogen Bonding Distance
The hydrogen bonding distance is influenced by several factors, including the electronegativity of the atoms involved, the hybridization state of the atoms, and the solvent effects. The electronegativity of the atoms determines the degree of charge transfer between the atoms, which in turn affects the hydrogen bonding distance. The hybridization state of the atoms also plays a crucial role, as it determines the directionality and strength of the hydrogen bond. Solvent effects, such as the polarity and dielectric constant of the solvent, can also influence the hydrogen bonding distance by modifying the electrostatic interactions between the atoms.
| Factor | Influence on Hydrogen Bonding Distance |
|---|---|
| Electronegativity | Decreases distance with increasing electronegativity |
| Hybridization state | Influences directionality and strength of hydrogen bond |
| Solvent effects | Modifies electrostatic interactions and distance |
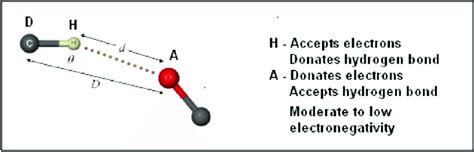
Methods for Determining Hydrogen Bonding Distance
Several methods are available for determining the hydrogen bonding distance, including X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and quantum mechanical calculations. X-ray crystallography provides accurate information on the atomic positions and bonding distances in crystals. NMR spectroscopy can provide information on the spin-spin coupling constants and chemical shifts, which can be used to estimate the hydrogen bonding distance. Quantum mechanical calculations, such as density functional theory (DFT), can provide accurate predictions of the hydrogen bonding distance and energy.
Applications of Hydrogen Bonding Distance
The understanding of hydrogen bonding distance has numerous applications in chemistry, biology, and materials science. In drug design, the hydrogen bonding distance is critical in predicting the binding affinity and specificity of drugs to their targets. In materials science, the hydrogen bonding distance is important in designing new materials with specific properties, such as self-healing materials and supramolecular materials. In biological systems, the hydrogen bonding distance plays a crucial role in understanding the structure and function of biomolecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
- Drug design: predicting binding affinity and specificity
- Materials science: designing new materials with specific properties
- Biological systems: understanding structure and function of biomolecules
What is the typical range of hydrogen bonding distances?
+The typical range of hydrogen bonding distances is between 1.5 and 3.5 Å, depending on the atoms involved and the solvent effects.
How does the electronegativity of atoms influence the hydrogen bonding distance?
+The electronegativity of atoms influences the hydrogen bonding distance by determining the degree of charge transfer between the atoms. A higher electronegativity typically results in a shorter hydrogen bonding distance.
In conclusion, understanding hydrogen bonding distance is essential for chemists and researchers, as it has significant implications for various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. The factors that influence hydrogen bonding distance, such as electronegativity, hybridization state, and solvent effects, must be carefully considered to predict the stability and reactivity of molecules. The methods for determining hydrogen bonding distance, including X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, and quantum mechanical calculations, provide accurate information on the atomic positions and bonding distances. The applications of hydrogen bonding distance are numerous, ranging from drug design to materials science and biological systems.


